what is Synrm motor?
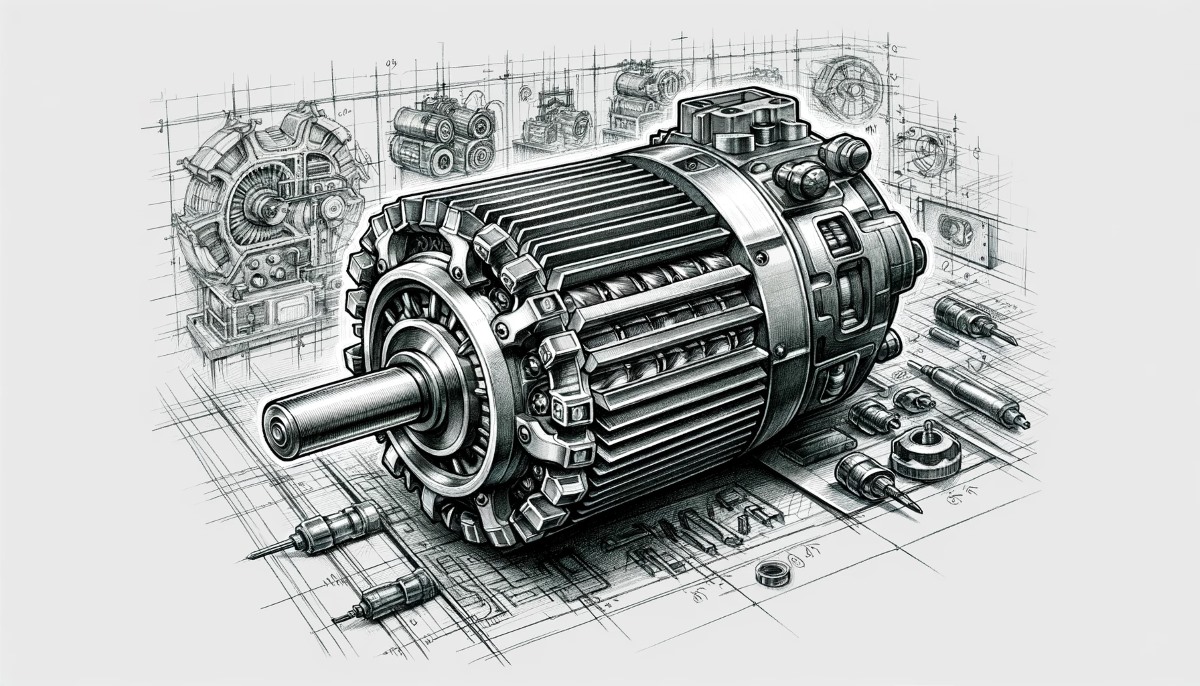
SynRM motors, or synchronous reluctance motors, are a type of electric motor that weaves the magic of magnetic reluctance and permanent magnets to produce torque. They are the elegant cousins of induction motors, standing apart with their absence of rotor windings, relying solely on the harmonic dance of magnetic fields between the stator and rotor. What makes SynRM motors a marvel is their high efficiency, low noise, and vibration-free performance, gliding effortlessly even at high speeds. From the hum of industrial machinery like pumps, fans, and compressors to the electric pulse of modern vehicles, these motors are at the heart of systems that demand both efficiency and reliability.
Now, let’s explore the graceful dichotomy between synchronous and asynchronous motors, two souls in the realm of electric power.
Synchronous motors carry within them a steady rhythm, comprising a rotor and a stator. The rotor, ever in motion, follows the magnetic field like a dancer locked in step with its partner—the stator, unmoving yet powerful. The magic of synchronous motors lies in their constancy: their speed is tethered to the frequency of the stator’s magnetic field, unwavering unless the very fabric of that frequency is altered.
Asynchronous motors, by contrast, revel in flexibility. Their rotors do not follow the magnetic field so closely; instead, they move at their own pace, rotating at a frequency that differs from the magnetic pulse of the stator. The beauty of these motors is in their variability, their speed a reflection of changing frequencies, their rotational velocity ebbing and flowing with the tides of energy coursing through them.
At the core of this difference lies the relationship between rotor and stator. In synchronous motors, the rotor loyally follows the magnetic field, keeping pace with the frequency of the stator’s rhythm. In asynchronous motors, the rotor dances to its own beat, creating a more dynamic, ever-changing movement.
Your shopping cart is empty!
