What is output filter?
An output filter for a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is an electrical device used to reduce the harmonic content of the voltage and current produced by the drive. Harmonics are high-frequency components of electrical waveforms that can lead to electrical noise, overheating of equipment, and power quality issues.
Output filters in VFDs usually consist of inductors (coils) and capacitors. The inductors help smooth the current waveform by filtering high-frequency harmonics, while capacitors stabilize voltage harmonics. By eliminating these distortions, an output filter not only improves power factor but also reduces unwanted electromagnetic interference (EMI), leading to more stable system performance.
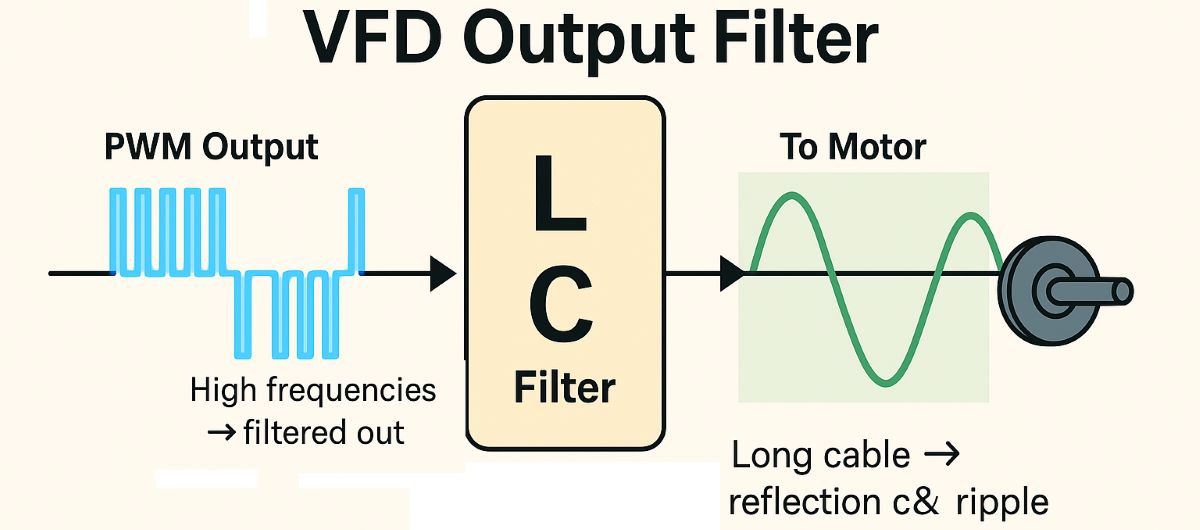
VFD Output Filter — From PWM to Sine Wave (educational simulation)
On the left, the PWM output appears; in the middle, the LC filter; and on the right, the clean sine wave delivered to the motor. Adjust the sliders to observe how Carrier Frequency, Filter Strength, and Cable Length affect the waveform. As the filter strength increases, high-frequency noise decreases. Longer cables create more reflection and distortion.
How to read: When Fc increases, the PWM pulses become narrower and the filter works harder. Increasing LC strength makes the output smoother. Longer cables cause ripple and reflection on the signal.
They are most commonly used in systems where the drive powers a large load—such as an industrial motor—where power stability and reliability are essential. Output filters can be applied to both AC and DC drives, and are available in a wide range of designs and ratings, depending on the system’s requirements.
The key takeaway is that an output filter acts as the silent guardian of your drive system. It ensures clean energy delivery to your motor, prevents high-frequency reflection on long cables, and significantly extends the lifespan of your VFD and connected components. Without it, even a perfectly tuned system may suffer from instability and premature wear.
In industrial environments where precision and uptime are critical, a properly designed output filter minimizes EMI disturbances that could disrupt sensors or PLC inputs. It transforms the rough PWM signal into a smoother sine-like waveform, resulting in quieter operation and reduced thermal stress on the motor windings.
Ultimately, investing in a good output filter is not just about compliance or efficiency — it’s about protecting your entire automation network. A well-filtered system runs cooler, cleaner, and longer, ensuring consistent performance even under harsh electrical conditions.
To control the interference from the output side of an inverter, there are several steps you can take:
Your shopping cart is empty!
